Managing cloud resources has really changed with the Infrastructure as Code (IaC) approach, and Terraform has become one of the best tools for the job. But as things get more complicated, it can be difficult to keep your Terraform code clean, efficient and secure. Just as software developers use tools such as linters and documentation generators, infrastructure engineers also need specific tools to ensure that their Terraform code is ready for production.
In this article, I’ll cover a few important tools that can help you keep your Terraform code in good shape. I’ll cover areas such as static analysis, documentation, security checks and ways to improve your workflow. These tools can alert you early on to potential problems, help you adhere to best practices, stimulate teamwork and reduce operational risks.
1 — Static Analysis and Linting with TFLint
What is TFLint?
TFLint is a powerful static analysis tool specifically designed for Terraform. Unlike Terraform’s built-in terraform validate command, which only checks syntax and basic structure, TFLint performs deeper analysis to identify potential errors, deprecated syntax, and provider-specific issues before you apply your infrastructure changes.
Key Benefits
- Provider-Specific Rules : TFLint includes rules tailored to major cloud providers like AWS, Azure, and GCP, catching issues such as using instance types that don’t exist in a specific region.
- Custom Rule Support : You can create organization-specific rules to enforce your internal standards and best practices.
- Integration with CI/CD Pipelines : TFLint can be easily integrated into your continuous integration workflows, preventing problematic code from reaching production.
Getting Started with Tflint
Installing TFLint is straightforward:
Create a .tflint.hcl configuration file in your project root to customize
rules:
| |
Run TFLint regularly during development:
| |
Output:
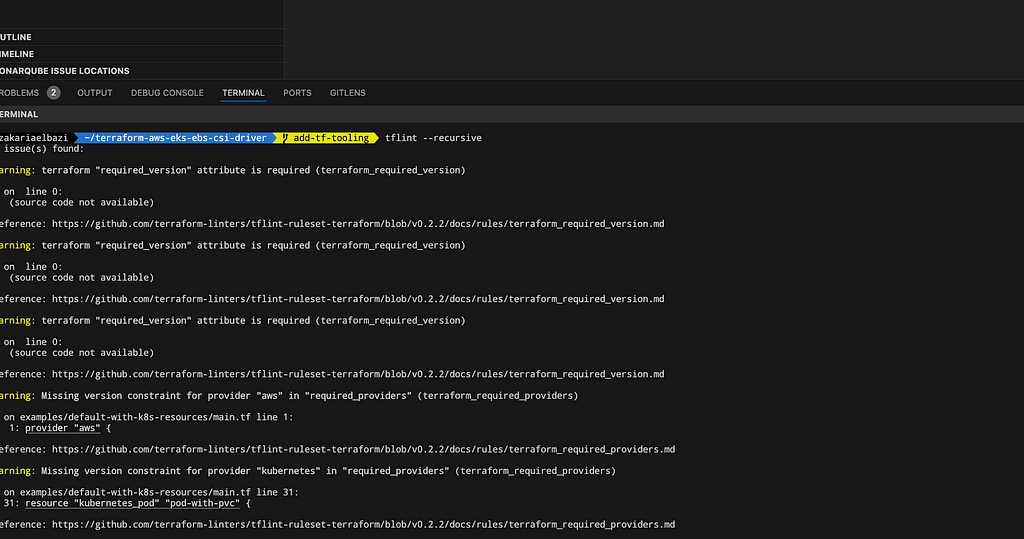 Tflint output for the module https://github.com/Z4ck404/terraform-aws-eks-ebs-csi-driver
Tflint output for the module https://github.com/Z4ck404/terraform-aws-eks-ebs-csi-driver
2 — Automated Documentation with terraform-docs
What is terraform-docs?
Terraform-docs automatically generates documentation from your Terraform code, helping team members understand the purpose, inputs, outputs, and dependencies of your modules without having to manually maintain README files.
Key Benefits
- Consistent Documentation : Ensures all modules are documented in a standard format.
- Always Up-to-Date : Documentation is generated directly from code, eliminating drift between documentation and implementation.
- Multiple Output Formats : Supports Markdown, JSON, YAML, and other formats to fit different needs.
Getting Started with terraform-docs
Install terraform-docs:
Create a .terraform-docs.yml configuration file:
Generate documentation with:
| |
The output :
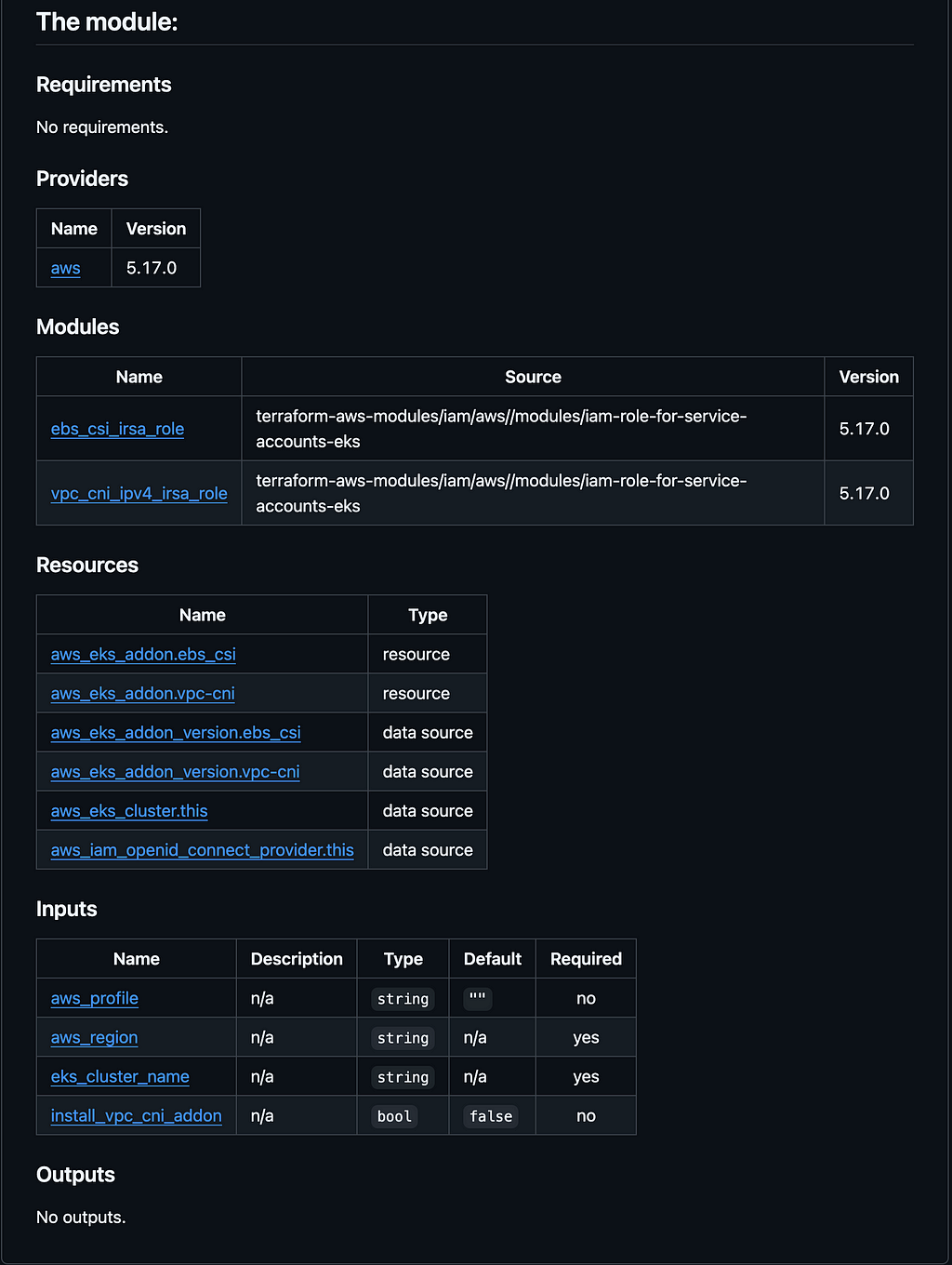
For Git repositories, consider using pre-commit hooks to automatically update documentation before each commit.
3 — Security Scanning with Terrascan and Trivy
3.1 — Terrascan
Terrascan is an open-source security vulnerability scanner for Infrastructure as Code that detects compliance and security violations to mitigate risk before provisioning infrastructure.
Key Features
- Comprehensive Policy Set : Includes hundreds of policies based on security best practices.
- Multiple IaC Support : Works with Terraform, Kubernetes, AWS CloudFormation, and more.
- Customizable Policies : Supports custom policies written in Rego (Open Policy Agent language).
Getting Started with terrascan
Install Terrascan:
Run a scan:
| |
3.2 — Trivy
Trivy is a comprehensive security scanner that can find vulnerabilities in container images, file systems, and configuration files including Terraform.
Key Features
- Wide Coverage : Scans for vulnerabilities in infrastructure code, container images, and more.
- Misconfigurations Detection : Identifies security issues in Terraform configurations.
- Fast and Easy to Use : Simple setup with minimal configuration required.
Getting Started with trivy
Install Trivy:
Scan Terraform files:
| |
Additional Essential Tools for Production-Ready Terraform
1 — tfenv — Terraform Version Manager
tfenv is a simple yet powerful tool that solves the common challenge of managing multiple Terraform versions across different projects and teams. Version compatibility issues can lead to frustrating errors and inconsistent behavior, making tfenv an essential addition to any serious Terraform workflow.
Key Features
- Simple Version Management : Install, uninstall, and switch between Terraform versions with simple commands.
- Project-Specific Versions : Automatically use the correct Terraform version for each project using .terraform-version files.
- Easy Installation : Works on macOS, Linux, and Windows (via Windows Subsystem for Linux).
Getting Started with tfenv
| |
Best Practices
- Version Pinning : Always specify the exact Terraform version in your .terraform-version file to ensure consistent behavior across all environments.
- CI/CD Integration : Configure your CI/CD pipelines to use tfenv to guarantee the correct Terraform version is used during automated deployments.
- Upgrade Testing : Use tfenv to test your Terraform configurations against new versions before officially upgrading.
A .terraform-version file in each project’s root directory allows tfenv to
automatically switch to the appropriate version when you change directories,
reducing the risk of applying infrastructure changes with an incorrect
Terraform version.
2 — Checkov
Checkov is a static code analysis tool for infrastructure as code that scans cloud infrastructure configurations to find misconfigurations before they’re deployed.
Key Features
- Extensive Policy Library : Includes over 1,000 built-in policies.
- Custom Policies : Supports Python-based custom policies.
- Skip Mechanism : Allows you to skip specific checks with justification.
Getting Started
3 — pre-commit Hooks
Pre-commit is a framework for managing and maintaining multi-language pre- commit hooks, which can automate formatting, linting, and documentation generation before code is committed.
Sample Configuration
Create a .pre-commit-config.yaml file:
| |
4 — Terragrunt
Terragrunt is a thin wrapper for Terraform that provides extra tools for working with multiple Terraform modules, fostering a DRY approach to Terraform code.
Key Features
- Configuration Reuse : Reduces repetition in Terraform configurations.
- Remote State Management : Simplifies backend configuration.
- Dependency Management : Handles dependencies between modules more elegantly.
Getting Started
5 — Infracost
Infracost shows cloud cost estimates for Terraform, helping engineers understand the financial implications of their infrastructure changes.
Key Features
- Cost Breakdowns : Detailed breakdowns of resources and their estimated costs.
- CI/CD Integration : Can run in CI/CD pipelines to show cost differences in pull requests.
- Multiple Cloud Provider Support : Works with AWS, Azure, GCP, and more.
Getting Started
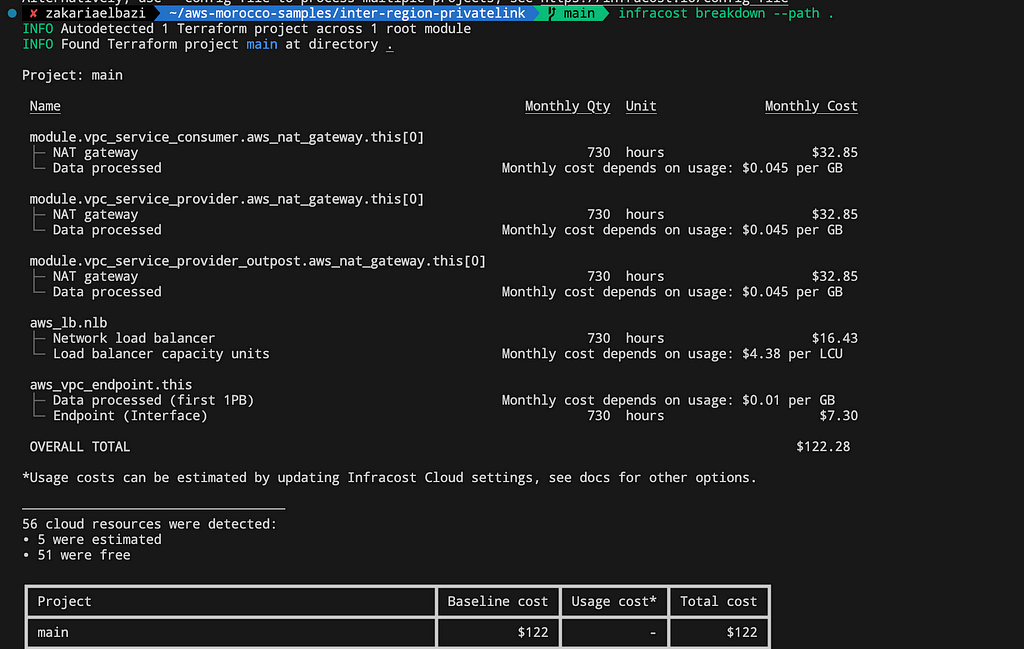 Infracost run against https://github.com/Z4ck404/aws-morocco-samples/tree/main/inter-region-privatelink
Infracost run against https://github.com/Z4ck404/aws-morocco-samples/tree/main/inter-region-privatelink
6 — Terraform Compliance
Terraform Compliance is a lightweight, compliance-focused test framework against Terraform that enables negative testing capability.
Key Features
- BDD-style Testing : Uses human-readable language for compliance rules.
- Focuses on Security : Specifically designed to enforce security and compliance requirements.
- CI/CD Integration : Can be integrated into CI/CD pipelines.
Example
Integrating These Tools into Your Workflow
To get the most benefit from these tools, integrate them into your development workflow:
- Local Development : Use pre-commit hooks to ensure code quality before commits.
- CI/CD Pipeline : Run all tools during your CI process to catch issues before they reach production.
- Code Reviews : Use generated reports as part of the pull request review process.
- Regular Audits : Schedule comprehensive scans of your entire infrastructure codebase weekly or monthly.
A sample CI/CD pipeline stage might look like:
Conclusion
In this article, we’ve looked at some practical tools that can help you keep your Terraform code in good shape. By using static analysis, automated documentation, security checks and cost estimation as part of your routine, you can catch errors early, meet your standards and keep your infrastructure safe and running smoothly.
By combining the right tools with code/infra best practices, you can create a sustainable infrastructure that’s scalable, secure and easy to manage.
What tools have you found useful on your Terraform journey? Please let me know in the comments! 💬
Terraform Infrastructure as Code: Essential Tools for Clean, MaintainableProduction Environments was originally published in AWSMorocco on Medium, where people are continuing the conversation by highlighting and responding to this story.