In the previous article (Part1), we installed the ELK stack along with the ES-Hadoop connector and spark, then we did some visualizations in Kibana with the houses price prediction data set from kaggle.
In this part we will start with adding Search Guard to the stack in order to define permissions and access to our data and configurations, then we will implement our models with the help of Spark Ml lib, and we will finish with deploying our models in a pipeline in order to predict the prices for new entries to our Elasticsearch.

I already talked about it in the part 1 of this series. Search Guard is an open source plugin for alerting and security for the elastic stack that comes with advanced security options to allow better integration in the various infrastructures that can be used with Elasticsearch. It adds security and encryption to Elasticsearch data and to communication both at the Transport and REST levels. Search Guard provides also a plugin for Kibana that adds a Search Guard GUI for security configuration (adding users, roles and performing roles mappings), and Signals configuration for alerting and monitoring watches
1 - Adding Search Guard to Elasticsearch :
Search Guard can be installed like any other Elasticsearch plugin by using the bin/elasticsearch-plugin command that ealsticsearch provides.
First we download the SG version matching our elasticsearch version :
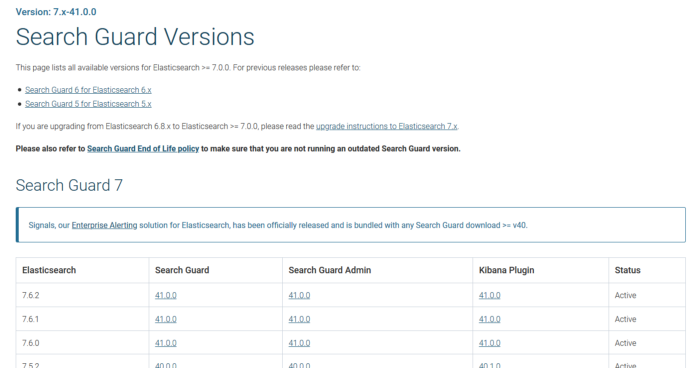
then cd to elasticsearch dir and type :
| |
It is also possible to install the plugin directly from SG releases server by specifying the URL like this:
| |
When the plugin is successfully downloaded and installed, we can either execute the demo installer that search guard comes with for demo purposes and easy PoC configuration by :
That will do the TLS setup by adding the demo TLS certificates to the config folder and adding the required configuration to elasticsearch.yml. It will also generate a sgadmin_demo.sh script that you can use for applying configuration changes on the command line.
NB : Any changes in the configuration files of Search Guard (sg_*.yml) will require executing sg_admin for these changes to take place (adding a user,role,etc.).
But for production it’s recommended to do a manual installation by using your own certificates (in case you already have them or use Search Guard TLS offline generator that you can find in tools folder ).
2 - Adding Search Guard to Kibana:
The Search Guard Kibana plugin adds authentication, multi tenancy and the Search Guard configuration GUI to Kibana. Installing it is pretty much easy using the kibana-plugin command. We download the kibana plugin matching our version of kibana, we cd to the kibana directory and we type :
| |
NB: You can also download the zip files and unzip them in the right folders for both elasticsearch and kibana (/plugins) !
once search guard is added and configured successfully, adding users, roles and defining security policies can be done using the sg_*.yml files with the help of sg_admin or by using the kibana GUI.
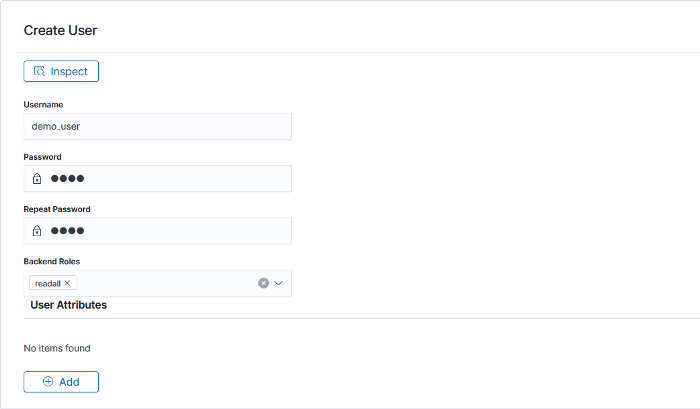
Let’s add a demo_user for this tutorial that we will use later to read data using es-hadoop :
- username : demo_user
- password: pass
NB : In case you couldn’t see the Search Guard icon in Kibana please refer to this page to solve the issue.
3 - Configuring ES-Hadoop with SG:
ES-hadoop as I mentioned in the part 1 is a sort of bridge that connects Elasticsearch with the Hadoop ecosystem so that they can benefit each other with distributed computing, distributed storage, distributed search and analytics and of course visualizations and real time dashboards.
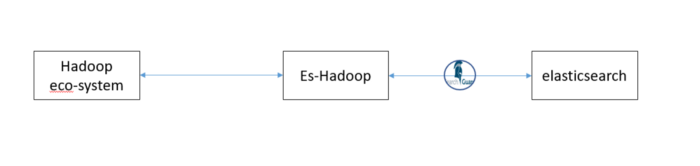
Elasticsearch-Hadoop is REST based which means it uses Elasticsearch REST interface for communication with Elasticsearch cluster, For that we won’t need any complicated configuration for spark in order to communicate with our secured es cluster.
First, let’s download es-Hadoop matching our Elasticsearch version (for this article I am using Elasticsearch 7.6.2) :
The spark Jar we need is located in the dist folder :
| |
Next, we will need to add some configuration to Spark :
| |
Save this configuration as a scala file (in this example spark_conf.scala) to execute it once or type the lines interactively is spark-shell.
Since we are using just HTTP Basic Auth with SG, all we need to setup is the user and password, but if you have other authentication/authorization mechanisms like client certificates, kerberos or whatever check the es-hadoop documentation for the instructions.
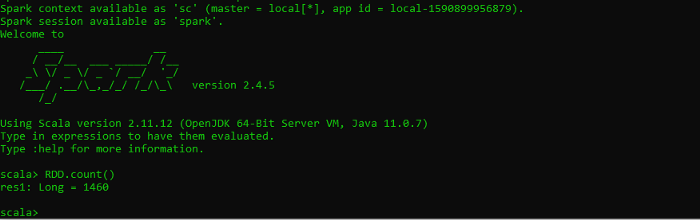
We will read thehousesindex in our elasticsearch to a Spark RDD and run the RDD.count() command to count the number of documents loaded :
| |
Search Guard is a trademark of floragunn GmbH, registered in the U.S. and in other countries. Elasticsearch, Kibana, Logstash, and Beats are trademarks of Elasticsearch BV, registered in the U.S. and in other countries. Apache, Apache Lucene, Apache Hadoop, Hadoop, Spark, Kafka, HDFS and the yellow elephant logo are trademarks of the Apache Software Foundation in the United States and/or other countries. Open Distro for Elasticsearch is licensed under Apache 2.0. All other trademark holders rights are reserved
Photo by Nik Shuliahin on Unsplash
